Creatine Phosphate Functions in the Cell by
Creatine phosphate functions in the muscle cell by ________. D storing energy that will be transferred to ADP to resynthesize ATP as needed.
Nutrients Free Full Text Role Of Creatine In The Heart Health And Disease Html
Creatine is naturally found in your muscles red meat and fish.

. Creatine phosphate CP functions within the muscle cells by ________. Creatinine phosphate functions in the muscle cells by storing energy that will be transferred to ADP to resynthesize ATP. Storing energy that will be transferred to ADP to resynthesize ATP.
Inducing a conformational change in the myofilaments. A forming a temporary chemical compound with myosin B forming a chemical compound with actin C inducing a conformational change in the myofilaments D storing energy that will be transferred to ADP to resynthesize ATP. Creatine is an amono acid which is produced by the liver kideny and pancreas.
Creatinine phosphate functions in the muscle cells by storing energy that will be transferred to ADP to resynthesize ATP. Asked Jun 13 2020 in Anatomy Physiology by John_Done. C inducing a conformational change in the myofilaments.
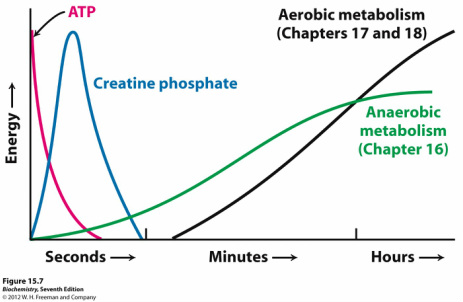
Normal metabolism can not produce energy as quickly as a muscle cell can use it so an extra storage source is needed. Storing energy that will be transferred to ADP to resynthesize ATP. Creatine kinase CK has several functions in cellular energy metabolism.
Creatine phosphate is the main high-energy phosphate-storage molecule of muscle. Creatine phosphate functions in the muscle cell by. How does creatine phosphate supply energy for muscle contraction.
Muscle cells use this phosphorylated form of creatine to store energy. 68 A storing energy that will be transferred to ADP to resynthesize ATP B inducing a conformational change in the myofilaments C forming a chemical compound with actin D forming a temporary chemical compound with myosin. Creatine phosphate is a phosphorylated creatine molecule.
B forming a chemical compound with actin. Creatine phosphate functions in the muscle cell by _____. During rest muscles are provided with energy through the normal.
Creatinine phosphate functions in the muscle cells by storing energy that will be transferred to ADP to resynthesize ATP. Reason- The major function of creatine phosphate is to act as reserve of energy primarily in the muscles and brain. Its used in muscle cells to store energy for sprinting and explosive exercise.
The phosphate group can be quickly transferred to ADP to regenerate the ATP necessary for muscle contraction. A forming a temporary chemical compound with myosin B inducing a conformational change in the myofilaments C forming a chemical compound with actin D storing energy that will be transferred to. Since muscles do not need much creatinine phosphate for energy.
Creatinine is stored as creatinine phosphate which is a source of ATP which in turn provides your body with energy. C inducing a conformational change in the myofilaments. Muscle cells use creatine phosphate to store high-energy phosphate bonds instead of ATP.
Storing energy that will be transferred to adp to resynthesize atp inducing a conformational change in the myofilaments forming a temporary chemical compound with myosin forming a chemical compound with actin. It provides inorganic phosphate to ADP Adenosine diphosphate to form ATP Adenosine triphosphat View the full answer. Forming a temporary chemical compound with myosin.
When the muscle starts to contract and needs energy creatine phosphate transfers its phosphate back to ADP to form ATP and creatine. During rest muscles are provided with energy through the normal. 13 Creatine phosphate functions in the muscle cell by _____.
In muscle cells this extra energy buffer plays a pivotal role in maintaining ATP homeostasis. Creatine shuttles high-energy phosphate from mitochondria our power producers to sites of. A forming a temporary chemical compound with myosin.
It is present in muscle cells for storing energy. Creatine phosphate functions in the muscle cell by _____. Energy is stored in creatine phosphate for rapid release.
Creatine phosphate functions in the muscle cell by _____. Creatine phosphate functions in the muscle cell by. Creatine phosphate functions in the muscle cell by storing energy that will be transferred to ADP to resynthesize ATP.
A forming a temporary chemical compound with myosin. The correct answer is option c. Creatine phosphate functions in the muscle cell by.
Muscle tissue contains enough creatine phosphate CP to sustain physical activity for up to 10 to 15 minutes. Creatinine is stored as creatinine phosphate which is a source of ATP which in turn provides your body with energy. Normal metabolism does not release energy as soon as released by creatine phosphate.
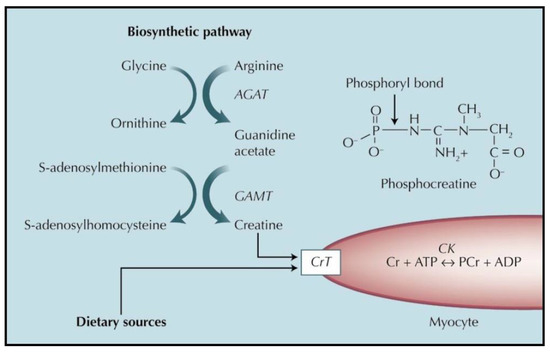
It catalyzes the reversible transfer of high-energy phosphate from ATP to creatine facilitating storage of energy in the form of phosphocreatine. B forming a chemical compound with actin. Creatine phosphate or phosphocreatine is a phosphorylated creatine molecule that serves as a rapid release reserve of high-energy.
In rested muscle creatine phosphate is the predominant form Demant and Rhodes 1999. Its maximal concentration is five times higher than that of ATP. This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme creatine kinase and.
Forming a chemical compound with actin. 68Creatine phosphate functions in the muscle cell by ________. Forming a chemical compound with actin B.
Phosphocreatine also known as creatine phosphate CP or PCr Pcr is a phosphorylated creatine molecule that serves as a rapidly mobilizable reserve of high-energy phosphates in skeletal muscle myocardium and the brain to recycle adenosine triphosphate the energy currency of the cell. During times of acute energy need the creatine kinase EC2732 uses creatine phosphate for the ultrarapid phosphorylation of. Creatinine is stored as creatinine phosphate which is a source of ATP which in turn provides your body with energy.
During muscle contraction ATP can be generated by the creatine phosphate pathway by cellular respiration and by Blank 1 of 1.

Muscle Fiber Contraction And Relaxation Anatomy And Physiology

Muscle Fiber Contraction And Relaxation Anatomy And Physiology

No comments for "Creatine Phosphate Functions in the Cell by"
Post a Comment